A new scientific article, published in npj Climate Action and authored by the Coordinating Lead Authors of the MedECC Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin, highlights an integrated approach to addressing the complex and interconnected challenges posed by climate change in the region.

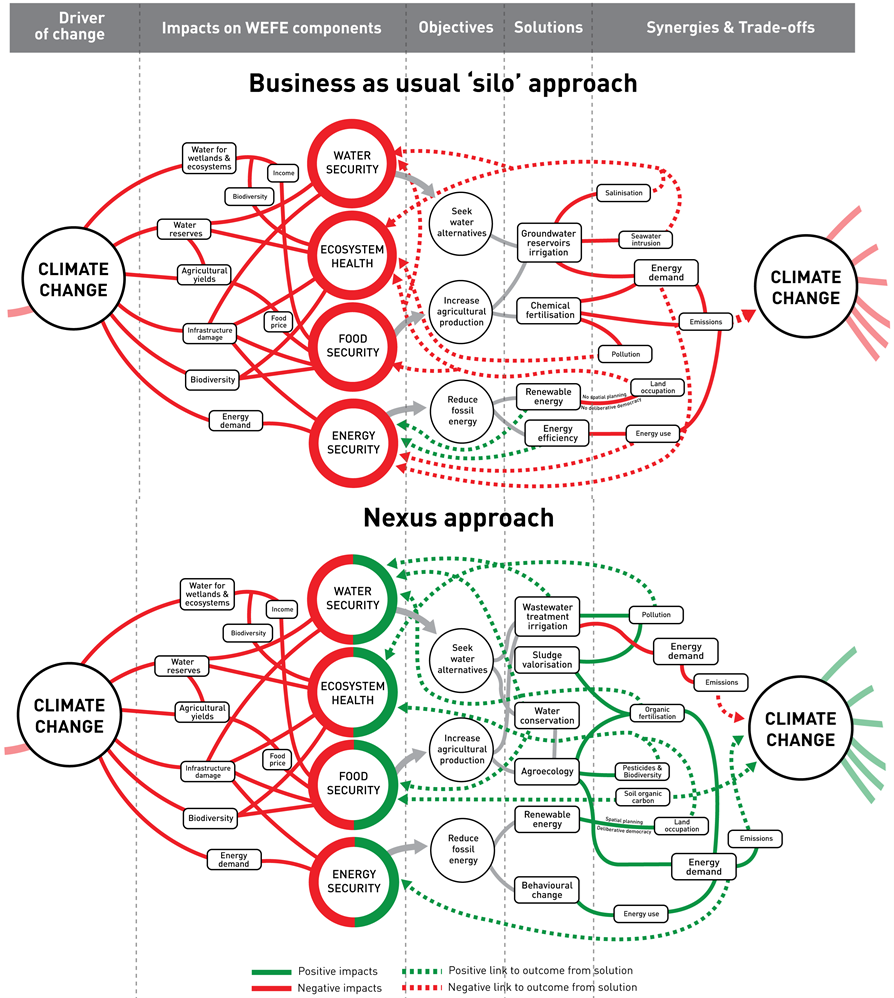
The Mediterranean region represents a climate change hotspot, characterised by the interaction of multiple intense climate hazards and by high levels of exposure and vulnerability. Rising temperatures, more frequent and intense droughts, and increasing pressure on natural resources threaten access to water, agricultural production, energy systems, and ecosystem health. Faced with the limitation of sector-specific responses, the authors chose to examine these challenges through the water-energy-food-ecosystems (WEFE) nexus. This integrated perspective helps identify the cascading impacts of climate change and avoid maladaptation. Their analysis shows that placing water at the center of action can strengthen cross-sectoral synergies and enhance regional resilience.
To reach this conclusion, the authors conducted a systematic review of recent scientific literature, complemented by the expertise of a multidisciplinary network spanning climate, agriculture, energy, and environment. They examined a wide range of solutions already implemented across Mediterranean countries – including technological innovations, agroecological practices, institutional arrangements, and behavioral changes – and assessed their effects on the four components of the nexus, as well as their capacity to limit climate impacts in cascade.
The results highlight that several types of actions – from nature-based solutions to technological innovations and shifts in consumption patterns – can become transformative if deployed within a coherent framework. They contribute to reducing pressure on water resources, greenhouse gas emissions, and ecosystem degradation, while also reinforcing food and energy security. These findings open opportunities for designing integrated, data-informed policies and guiding adaptation strategies in other regions facing similar climatic conditions.
How to cite this article: Drobinski, P., Rivera Ferre, M.G., Monem, M.A. et al. Nexus approach to enhance water-energy-food security and ecosystems resilience under climate change in the Mediterranean. npj Clim. Action 4, 115 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44168-025-00308-4
Discover the full report (english), summary for policymakers (english, french, arabic, catalan, spanish) and its visual summaries (french and english) here: Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water – Energy – Food – Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin – MedECC

